Dr Ronald Chin’s Take On Vestibular Disorders
Vestibular disorders disturb the body’s balance system. This is caused by some sort of damage in the vestibular system of the inner ear, the central nervous system processing systems, or even both.

Vestibular disorders disturb the body’s balance system. This is caused by some sort of damage in the vestibular system of the inner ear, the central nervous system processing systems, or even both.

The first step in epley manoevure is the Dix-Hallpike test.

The first step in epley manoevure is the Dix-Hallpike test.
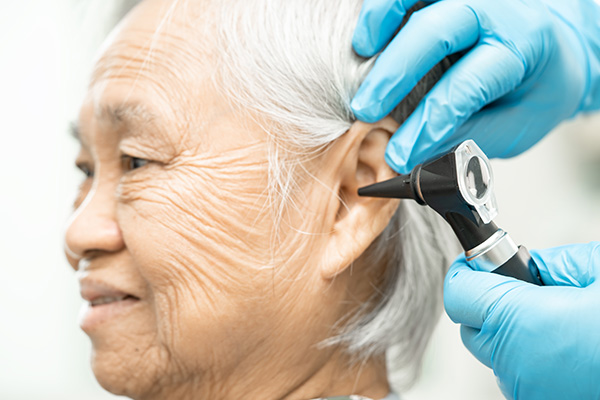
An “uncontrolled” immune system response is the defining characteristic of autoimmune inner ear disease, which is characterized by bilateral sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL).

Several drugs can lead to toxic damage to the inner ear, affecting hearing and vestibular function. The effects might not always be reversible.
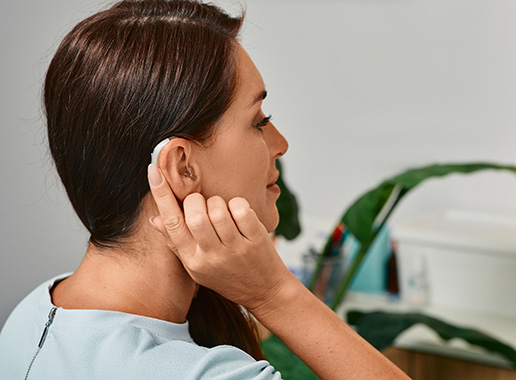
Congenital sensorineural hearing loss is an inner ear hearing loss that is present at birth. It can be either hereditary or non-hereditary. The hereditary defects can be classified as non-syndrome-associated and syndrome-associated.
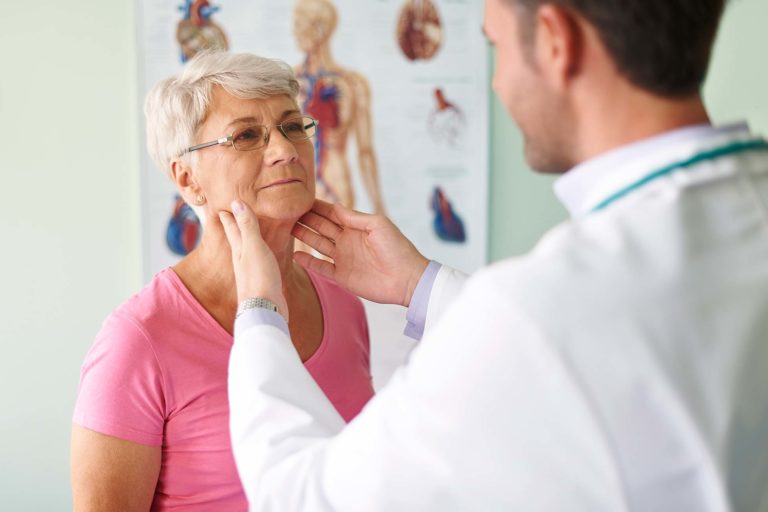
Presbycusis is an age-related sensorineural hearing loss disease. This is more common in men than women. By the age of 75, more than half of the adult population is impacted by it.

Congenital sensorineural hearing loss is an inner ear hearing loss that is present at birth. It can be either hereditary or non-hereditary. The hereditary defects can be classified as non-syndrome-associated and syndrome-associated.

Otosclerosis is the bony overgrowth of the stapes footplate, leading to fixation and conductive hearing loss. Symptoms for this include slow progressive hearing loss in both ears, increased vascularity of the middle ear, bony prominence, and tinnitus might also be seen.
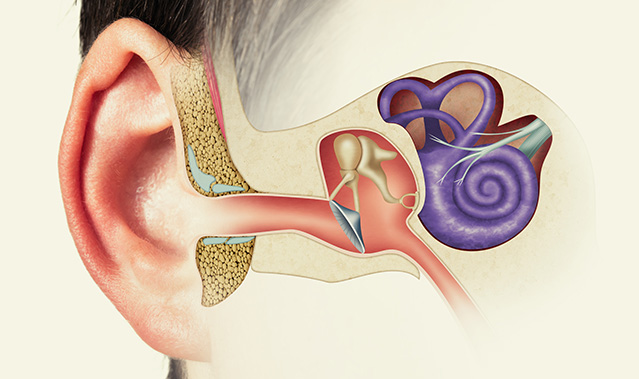
Otosclerosis happens when abnormal bone growth occurs in the middle or inner ear, causing interference with sound traveling to your ear. Otosclerosis can lead to conductive hearing loss.
End of content
End of content