Tinnitus: Ringing In The Ears And What To Do About It
Tinnitus: Ringing In The Ears And What To Do About It
You’ve probably heard about it. The ear disease causes victims to continuously hear a white noise – without an off button. There’s no stopping it. Sounds like a nightmare, right?
Well, that’s what it’s like to live with tinnitus. An anomaly to the natural hearing process. Something that can make life a living nightmare, whether you’re awake or asleep.
Tinnitus is an affliction where a person experiences phantom sounds in one or both ears. It’s a symptom that can appear for many reasons, the most common being hearing loss due to age. While there’s no cure for tinnitus, there are treatments that can lessen the condition.
Let’s find out more about this disease, what causes it, and how it can be prevented.
Let’s dive in.
So What is Tinnitus?
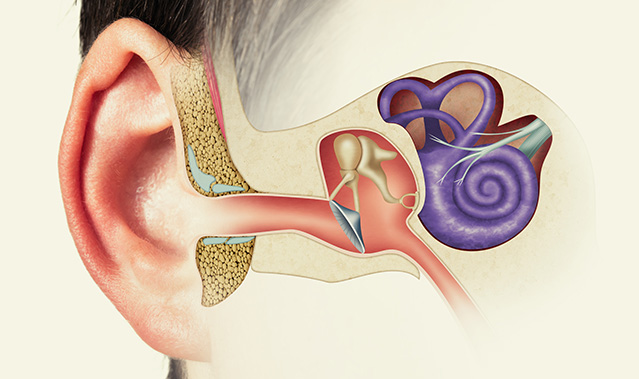
Tinnitus is the term used to describe the sensation of hearing phantom sounds in one or both ears. The sounds are subjective, meaning they can only be heard by the person suffering from tinnitus. Tinnitus can appear in varying levels of severity. Some people may experience a tiny ringing sound, while others report hearing a loud roaring noise.
What Are The Causes of Tinnitus?
Tinnitus can have many causes, the most common being age-related hearing loss. However, there are many different causes of tinnitus, but most commonly, it’s caused by damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve. This damage can be caused by a number of things, including exposure to loud noise, the use of certain medications, and head or neck injuries.
The most common causes include –
- Exposure to loud noises
- Earwax buildup
- Ear bone changes
- Meniere’s disease
- Tumors on the auditory nerve
- Migraines
- High blood pressure
- Thyroid problems
- Side effects from certain medications
The 4 Types of Tinnitus
- Subjective tinnitus: This type of tinnitus is characterized by a sound that can only be heard by the person with tinnitus. This type of tinnitus is usually caused by an injury to the inner ear or auditory nerve. It can also happen from loud noises.
- Sensory tinnitus: This is a condition where a person experiences ringing in their ears even when no external sound is present. This can be caused by damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve or by a problem with the brain’s ability to process auditory information.
There is no cure for sensory tinnitus, but there are treatments that can help lessen the symptoms. These include sound therapy, where the person is exposed to calming or distracting noises, and counseling, which can help them manage their stress and anxiety levels.
- Somatic tinnitus: Somatic tinnitus is a condition in which people hear phantom sounds that are not caused by an external source. These sounds may be ringing, buzzing, or clicking, and they can be loud or soft.
Somatic tinnitus is often caused by problems with the muscles, joints, or blood vessels in the head or neck. Some people with somatic tinnitus may also have other conditions, such as anxiety or depression. - Objective tinnitus: This type of tinnitus is characterized by a sound that can be heard by other people in addition to the person with tinnitus. This type of tinnitus is usually caused by a physical condition, such as a heartbeat or vascular anomaly.
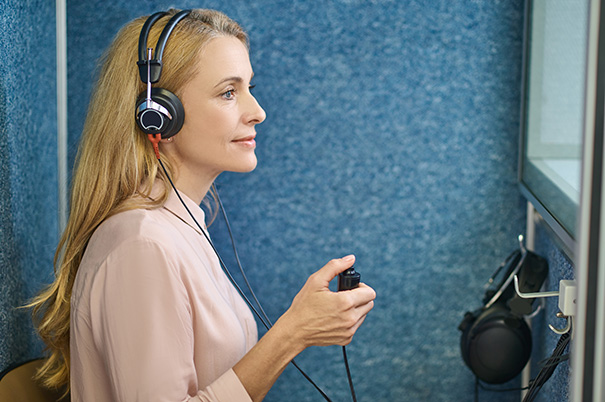
How is Tinnitus Diagnosed?
Tinnitus is diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and sometimes special tests.
During the medical history, your doctor will ask questions about your symptoms, when they began, and whether they come and go or are constant. Your doctor will also ask whether you have any other health problems and whether you take any medications.
During the physical examination, your doctor will examine your head and neck to look for any structural problems. He or she will also use a stethoscope to check for any abnormal sounds in your ears.
Special tests may be needed if your doctor suspects you have a problem with your middle ear or auditory nerve. These tests may include an MRI or CT scan of your head, auditory brainstem response (ABR) testing, or an electronystagmogram (ENG).
How is Tinnitus Treated?
There is no cure for tinnitus, but there are treatments that can lessen the symptoms. Treatments include:
Sound-masking devices: These devices produce low-level noise that can help to cover up the phantom sounds of tinnitus. White noise-creating machines create static noise continuously, and many people have found it helpful. They use it during the night to ignore the phantom noise.
Hearing aids: If tinnitus is caused by hearing loss, hearing aids can help to amplify sounds and make them less noticeable.
Relaxation techniques: Relaxation techniques such as yoga or meditation can help to reduce stress and anxiety, which can worsen tinnitus symptoms.
Tinnitus retraining therapy: This therapy uses a combination of counseling and sound-generating devices to help the brain learn to ignore the phantom sounds of tinnitus.
Cognitive behavioral therapy: This can help people change the way they think about and react to tinnitus.
Surgery: In rare cases, surgery may be necessary to correct an underlying cause of tinnitus, such as a tumor.
When to See a Doctor?
Tinnitus can be a symptom of a more serious condition, so it’s important to see a doctor if you are concerned.
If you have tinnitus, you should see a doctor if –
- The ringing lasts for more than a few minutes
- The ringing occurs frequently
- The ringing affects your quality of life
To Wrap It Up
This is one of the weirdest, most annoying, yet harmless diseases one can have. No changes in your life other than the continuous phantom noise you’ll be hearing. Whether you’re up, asleep, or trying to sleep.
The worst part is that there’s no definitive cure for it. One can only pray it doesn’t happen to him. However, even if it happens to you, don’t panic because there is treatment. Not a 100% cure, however, there are ways to make the situation more bearable for you.
So, don’t lose hope.
Glue ear, after draining the ear drum
Glue ear, intact ear drum
- About the Author
- Latest Posts
Dr Ronald Chin is an Australian trained Otolaryngologist Head and Neck Surgeon.
After graduating as a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons, Dr Chin undertook further specialised training in Head and Neck Cancer at the Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland.
He has published many research papers and is an active teacher and scholar.
As part of his subspecialty training, Dr Chin has training in Laser, Da Vinci Robotic, Flex Robotic and complex surgical techniques.
In addition to specialised Head and Neck Cancer, Dr Chin also enjoys general adult and paediatric ENT Surgery and practices sinus, snoring/sleep and general paediatric ENT Surgical procedures.
Dr Ronald Chin works as a general Otolaryngologist, offering a wide range of surgical and non-surgical treatments including ear surgery, nose surgery and throat surgery. He provides treatment for chronic conditions such as tonsillitis, sinus problems and problems with hearing.
He is also involved in the diagnosis and treatment of many conditions such as facial paralysis, head and neck cancer and sleep apnea. As well as performing surgery on children, he also provides specialist care for adults, including the treatment of throat disorders, voice loss and ear problems.
Dr Chin has also served as a Conjoint Associate Professor at the University of Sydney, a Conjoint Associate Professor at Western Sydney University and an Adjunct Associate Professor at the University of Technology Sydney.